How many layers are in OSI reference model || OSI संदर्भ मॉडल में कितनी परतें हैं
OSI reference model: OSI reference model is an ISO standard which defines a networking framework for implementing the protocols in seven layers. These seven layers can be grouped into three categories:
- Network layer: Layer 1, Layer 2 and layer 3 are the network layers.
- Transport layer: Layer 4 is a transport layer.
- Application layer. Layer 5, Layer 6 and Layer 7 are the application layers.
There are 7 layers in the OSI reference model.
1. Physical Layer
- It is the lowest layer of the OSI reference model.
- It is used for the transmission of an unstructured raw bit stream over a physical medium.
- Physical layer transmits the data either in the form of electrical/optical or mechanical form.
- The physical layer is mainly used for the physical connection between the devices, and such physical connection can be made by using twisted-pair cable, fibre-optic or wireless transmission media.
2. DataLink Layer
- It is used for transferring the data from one node to another node.
- It receives the data from the network layer and converts the data into data frames and then attach the physical address to these frames which are sent to the physical layer.
- It enables the error-free transfer of data from one node to another node.
Functions of Data-link layer:
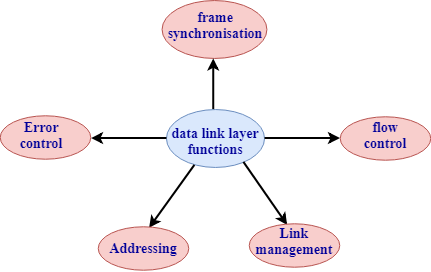
- Frame synchronization: Data-link layer converts the data into frames, and it ensures that the destination must recognize the starting and ending of each frame.
- Flow control: Data-link layer controls the data flow within the network.
- Error control: It detects and corrects the error occurred during the transmission from source to destination.
- Addressing: Data-link layer attach the physical address with the data frames so that the individual machines can be easily identified.
- Link management: Data-link layer manages the initiation, maintenance and, termination of the link between the source and destination for the effective exchange of data.
3. Network Layer
- Network layer converts the logical address into the physical address.
- It provides the routing concept means it determines the best route for the packet to travel from source to the destination.
Functions of network layer:
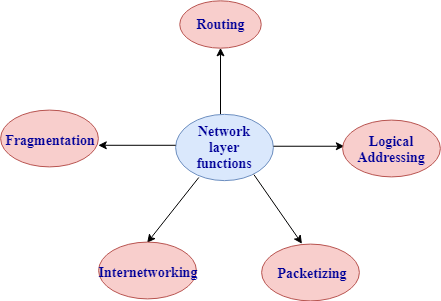
- Routing: The network layer determines the best route from source to destination. This function is known as routing.
- Logical addressing: The network layer defines the addressing scheme to identify each device uniquely.
- Packetizing: The network layer receives the data from the upper layer and converts the data into packets. This process is known as packetizing.
- Internetworking: The network layer provides the logical connection between the different types of networks for forming a bigger network.
- Fragmentation: It is a process of dividing the packets into the fragments.
4. Transport Layer
- It delivers the message through the network and provides error checking so that no error occurs during the transfer of data.
- It provides two kinds of services:
- Connection-oriented transmission: In this transmission, the receiver sends the acknowledgement to the sender after the packet has been received.
- Connectionless transmission: In this transmission, the receiver does not send the acknowledgement to the sender.
5. Session Layer
- The main responsibility of the session layer is beginning, maintaining and ending the communication between the devices.
- Session layer also reports the error coming from the upper layers.
- Session layer establishes and maintains the session between the two users.
6. Presentation Layer
- The presentation layer is also known as a Translation layer as it translates the data from one format to another format.
- At the sender side, this layer translates the data format used by the application layer to the common format and at the receiver side, this layer translates the common format into a format used by the application layer.
Functions of presentation layer:- Character code translation
- Data conversion
- Data compression
- Data encryption
7. Application Layer
- Application layer enables the user to access the network.
- It is the topmost layer of the OSI reference model.
- Application layer protocols are file transfer protocol, simple mail transfer protocol, domain name system, etc.
- The most widely used application protocol is HTTP(Hypertext transfer protocol ). A user sends the request for the web page using HTTP.
Join the conversation