exit command in Linux with Examples
exit command in linux is used to exit the shell where it is currently running. It takes one more parameter as [N] and exits the shell with a return of status N. If n is not provided, then it simply returns the status of last command that is executed.
Syntax:
exit [n]
Options for exit command –
- exit: Exit Without Parameter

After pressing enter, the terminal will simply close. - exit [n] : Exit With Parameter

After pressing enter, the terminal window will close and return a status of 110. Return status is important because sometimes they can be mapped to tell error, warnings and notifications. For example generally, return status –
“0” means the program has executed successfully.
“1” means the program has minnor errors. - exit n : Using “sudo su” we are going to the root directory and then exit the root directory with a return status of 5. After returning it will show how to display the return status code.
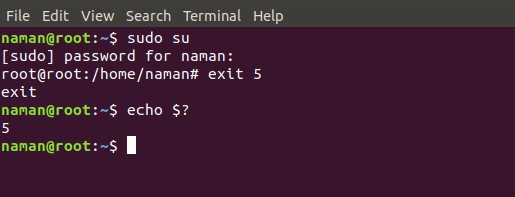
echo $?command is used to see the last return status. - exit –help : It displays help information.

Join the conversation