11 Class Chapter 1- Some Basic Concept of Chemistry
Classification of matter: -
1. Mixture:
a.
Homogeneous mixture
b.
Heterogeneous mixture
2. Pure substance:
a.
Elements
b.
Compounds
1. Mixture: - It contains two or more
substances in any ration known as its components.
Ex: - air, tea etc.
a.
Homogeneous mixture:- its components are
completely mix with each other and have uniform composition throughout the
solution.
Ex:- sugar solution, air.
b.
Heterogeneous mixture:- its components do not
have uniform composition throughout solution sometimes different components
observed.
Ex:- mixture of salt & sugar, sand & soil.
2. Pure substances:- these have fixed
composition.
Ex:- copper, gold, water etc.
a. Elements:- It consists of only one type
of particles (i.e. atoms or
molecules)
Ex:- H2, O2, Au, Ag.
b. Compounds:- It consist of two or more
atoms to give a molecule of compound
Ex:- CO2, NH3, H2O.
Properties of matter
1) Physical properties:- Those properties
which can be measured or observed.
2) Chemical properties:- those properties
in which chemical changes occurs.
Ex:-
Acidity, Basicity, Combustibility etc.
SI :- International System of units
Ø
Established by 11th general
conference on weight and measures.
Ø
Si have seven fundamental units
Ø
Other units are divided from seven fundamental
units
SI Table
Base physical quantity
|
Symbol for quantity
|
SI units name
|
SI units symbol
|
Length
|
l
|
Metre
|
m
|
Mass
|
m
|
Kilogram
|
Kg
|
Time
|
t
|
Second
|
s
|
Current
|
I
|
Ampere
|
A
|
Temperature
|
T
|
Kelvin
|
K
|
Amount of substance
|
n
|
Mole
|
Mol
|
Luminous intensity
|
Iv
|
candela
|
Cd
|
Prefixes for SI Units
Multiple
|
Prefix
|
Symbol
|
10-24
|
Yocto
|
y
|
10-21
|
Zepto
|
z
|
10-18
|
Atto
|
a
|
10-15
|
Femto
|
f
|
10-12
|
Pico
|
p
|
10-9
|
Nano
|
n
|
10-6
|
Micro
|
m
|
10-3
|
Milli
|
m
|
10-2
|
Centi
|
c
|
10-1
|
Deci
|
d
|
10
|
Deca
|
da
|
102
|
Hecto
|
h
|
103
|
Kilo
|
k
|
106
|
Mega
|
M
|
109
|
Giga
|
G
|
1012
|
Tera
|
T
|
1015
|
Peta
|
P
|
1018
|
Exa
|
E
|
1021
|
Zeta
|
Z
|
1024
|
yotto
|
Y
|
Mass:- amount of matter in object
=>
1 kg = 1000 gram
Weight: -force on the object by gravity.
Volume:- (length)3
=>
1 L = 1000 ml, 1000 cm3 = 1dm3
Density:- Amount of mass per unit volume.
=>
SI unit :- Kgm-3
Temperature:- It is the measurement of cooling or warming.
Three scales
=>
0C (Degree Celsius)
=>
0F degree Fahrenheit)
=>
k (Kelvin)
=>
freezing point of water = 0 0C
=>
Boiling point of water = 100 0C
Relationship
Or,
k = 0C +
273.15
Precision:- Closeness
of various measurement for same quantity.
Accuracy:- It is the
agreement of a particular value to the true value of the result.
Significant figure:-
The meaningful digits which are known with certainty.
Laws of chemical combinations
1) Law of conservation of mass:- According
to this law “matter can neither be created nor destroyed” Given by Antone Lovoisin in 1789.
2) Law of definite proportion:-
According to this law “A given compound always contains exactly the same
proportion of elements by weight known as law of definite proportion or law of definite composition” given by Joseph Proust in 1754-1826
3) Law of multiple proportion:-
According to this law “if two elements combine to form more than one compound,
the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of small whole number”
given by Dalton in 1803.
4) Gay lussac’s law of gaseous volume:- According
to this law “gases combine or are produced in chemical reactions they do so in
a simple ratio by volume provided to all gases are at the same temperature and pressure” given by Gay Lussac’s in 1808.
5) Avogadro’s law:- According
to this law “Equal volume of gases at same temperature & pressure should
contain equal no. of molecules” given by Avogadro
in 1811.
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
i.
Matter consists of indivisible atoms.
ii.
All the atoms of a element have identical
properties (same properties) i.e. atoms of a element have same mass while atoms
of different elements have different masses.
iii.
Compounds formed when atoms of different
elements combine in fixed ratio.
iv.
Chemical reactions involve reorganization
(rearrangement) of atoms.
Atomic mass unit = 1/12th
mass of one carbon12 atom.
Molecular mass = It is
the sum of atomic masses of the elements present in a molecule.
Mole :- It is the
amount of substance equal to Avogadro no. (NA). = 6.022 ´ 1023 atoms/mole.
Molar mass:- Mass of
one mol of a substances in gram is known as molar mass.
Mass % of an element =
mass of that element in compound ´
100/ molar mass of the compound.
Empirical formula :- It
is the simplest whole no. ratio of various atoms present in a compound.
Molecular formula:- It
is the exact no. of different types of atoms present in a molecule of a
compound.


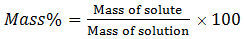

Join the conversation